SpectroChemPy Overview
Welcome to SpectroChemPy! This tutorial will give you a quick overview of the main features and capabilities of the library. We’ll cover:
Loading and displaying spectroscopic data
Basic data manipulation and plotting
Processing techniques (smoothing, baseline correction)
Advanced analysis methods
For more detailed information, check out:
Getting Started
First, let’s import SpectroChemPy. By convention, we use the alias scp:
[1]:
import spectrochempy as scp
|
|
SpectroChemPy's API - v.0.7.1 © Copyright 2014-2025 - A.Travert & C.Fernandez @ LCS |
Working with NDDataset Objects
The NDDataset is the core data structure in SpectroChemPy. It’s designed specifically for spectroscopic data and provides:
Multi-dimensional data support
Coordinates and units handling
Built-in visualization
Processing methods
Let’s load some example FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) data:
[2]:
ds = scp.read("irdata/nh4y-activation.spg")
Exploring Your Data
SpectroChemPy provides multiple ways to inspect your data. Let’s look at:
Basic information summary
Detailed metadata
[3]:
# Quick overview
scp.set_loglevel("INFO") # to see information
scp.info_(ds)
NDDataset: [float64] a.u. (shape: (y:55, x:5549))
[4]:
# Detailed information
ds
[4]:
| name | nh4y-activation |
| author | runner@fv-az1774-299 |
| created | 2025-02-25 08:00:03+00:00 |
| description | Omnic title: NH4Y-activation.SPG Omnic filename: /home/runner/.spectrochempy/testdata/irdata/nh4y-activation.spg |
| history | 2025-02-25 08:00:03+00:00> Imported from spg file /home/runner/.spectrochempy/testdata/irdata/nh4y-activation.spg. 2025-02-25 08:00:03+00:00> Sorted by date |
| DATA | |
| title | absorbance |
| values | [[ 2.057 2.061 ... 2.013 2.012] [ 2.033 2.037 ... 1.913 1.911] ... [ 1.794 1.791 ... 1.198 1.198] [ 1.816 1.815 ... 1.24 1.238]] a.u. |
| shape | (y:55, x:5549) |
| DIMENSION `x` | |
| size | 5549 |
| title | wavenumbers |
| coordinates | [ 6000 5999 ... 650.9 649.9] cm⁻¹ |
| DIMENSION `y` | |
| size | 55 |
| title | acquisition timestamp (GMT) |
| coordinates | [1.468e+09 1.468e+09 ... 1.468e+09 1.468e+09] s |
| labels | [[ 2016-07-06 19:03:14+00:00 2016-07-06 19:13:14+00:00 ... 2016-07-07 04:03:17+00:00 2016-07-07 04:13:17+00:00] [ vz0466.spa, Wed Jul 06 21:00:38 2016 (GMT+02:00) vz0467.spa, Wed Jul 06 21:10:38 2016 (GMT+02:00) ... vz0520.spa, Thu Jul 07 06:00:41 2016 (GMT+02:00) vz0521.spa, Thu Jul 07 06:10:41 2016 (GMT+02:00)]] |
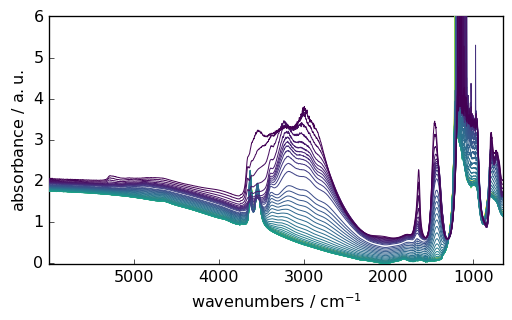
Data Visualization
SpectroChemPy’s plotting capabilities are built on matplotlib but provide spectroscopy-specific features:
[5]:
_ = ds.plot()
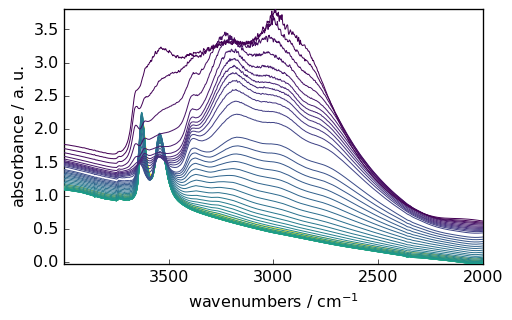
Data Selection and Manipulation
You can easily select specific regions of your spectra using intuitive slicing. Here we select wavenumbers between 4000 and 2000 cm⁻¹:
[6]:
region = ds[:, 4000.0:2000.0]
_ = region.plot()
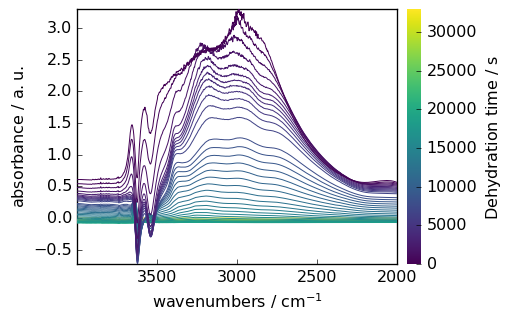
Mathematical Operations
NDDataset supports various mathematical operations. Here’s an example of baseline correction:
[7]:
# Make y coordinate relative to the first point
region.y -= region.y[0]
region.y.title = "Dehydration time"
# Subtract the last spectrum from all spectra
region -= region[-1]
# Plot with colorbar to show intensity changes
_ = region.plot(colorbar=True)
Data Processing Techniques
SpectroChemPy includes numerous processing methods. Here are some common examples:
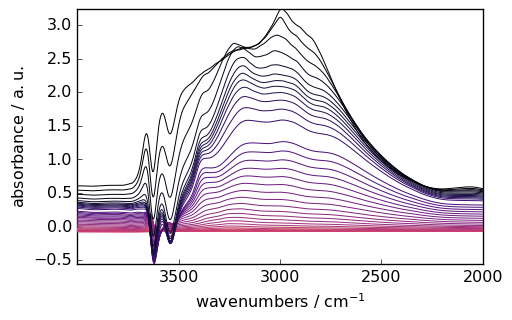
1. Spectral Smoothing
Reduce noise while preserving spectral features:
[8]:
smoothed = region.smooth(size=51, window="hanning")
_ = smoothed.plot(colormap="magma")
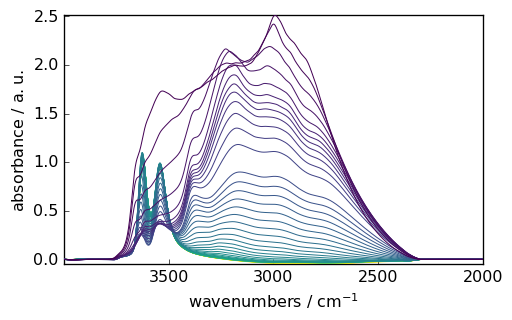
2. Baseline Correction
Remove baseline artifacts using various algorithms:
[9]:
# Prepare data
region = ds[:, 4000.0:2000.0]
smoothed = region.smooth(size=51, window="hanning")
# Configure baseline correction
blc = scp.Baseline()
blc.ranges = [[2000.0, 2300.0], [3800.0, 3900.0]] # Baseline regions
blc.multivariate = True
blc.model = "polynomial"
blc.order = "pchip"
blc.n_components = 5
# Apply correction
_ = blc.fit(smoothed)
_ = blc.corrected.plot()
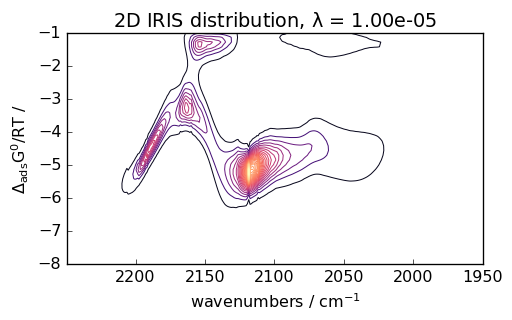
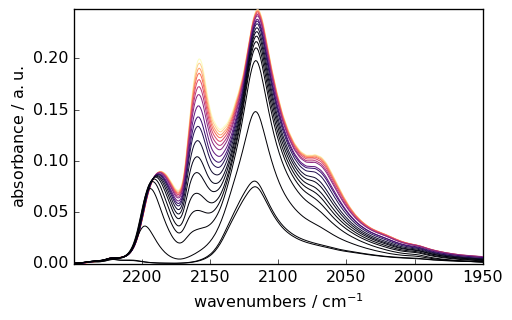
Advanced Analysis as for instance IRIS Processing
IRIS (Iterative Regularized Inverse Solver) is an advanced technique for analyzing spectroscopic data. Here’s an example with CO adsorption data:
[10]:
# Load and prepare CO adsorption data
ds = scp.read_omnic("irdata/CO@Mo_Al2O3.SPG")[:, 2250.0:1950.0]
# Define pressure coordinates
pressure = [
0.00300,
0.00400,
0.00900,
0.01400,
0.02100,
0.02600,
0.03600,
0.05100,
0.09300,
0.15000,
0.20300,
0.30000,
0.40400,
0.50300,
0.60200,
0.70200,
0.80100,
0.90500,
1.00400,
]
ds.y = scp.Coord(pressure, title="Pressure", units="torr")
# Plot the dataset
_ = ds.plot(colormap="magma")
[11]:
# Perform IRIS analysis
iris = scp.IRIS(reg_par=[-10, 1, 12])
K = scp.IrisKernel(ds, "langmuir", q=[-8, -1, 50])
iris.fit(ds, K)
_ = iris.plotdistribution(-7, colormap="magma")