spectrochempy.EFA
- class EFA(*, log_level='WARNING', warm_start=False, cutoff=None, n_components=None)[source][source]
Evolving Factor Analysis (EFA).
Evolving factor analysis (
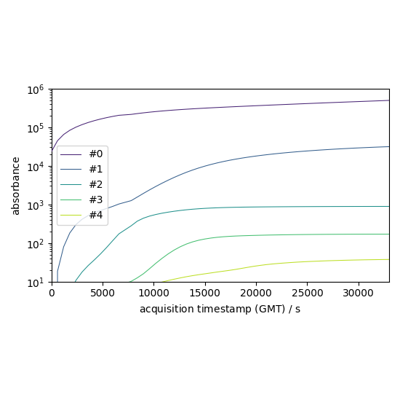
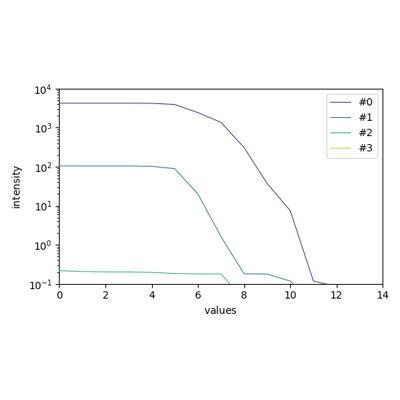
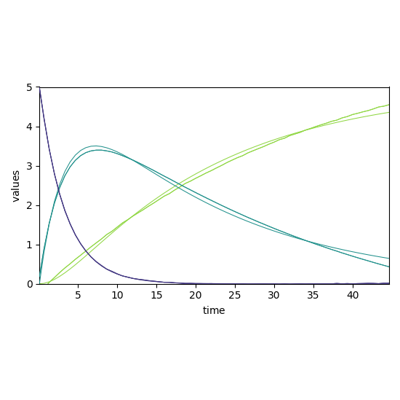
EFA) is a method that allows model-free resolution of overlapping peaks into concentration profiles and normalized spectra of components.Originally developed for GC and GC-MS experiments (See e.g., Maeder and Zuberbuehler [1986] , Roach and Guilhaus [1992]), it is also suitable for analysis spectra such as those obtained by Operando FTIR for example.
The model used in this class allow to perform a forward and reverse analysis of the input
NDDataset.- Parameters:
log_level (any of [
"INFO","DEBUG","WARNING","ERROR"], optional, default:"WARNING") – The log level at startup. It can be changed later on using theset_log_levelmethod or by changing thelog_levelattribute.warm_start (
bool, optional, default:False) – When fitting repeatedly on the same dataset, but for multiple parameter values (such as to find the value maximizing performance), it may be possible to reuse previous model learned from the previous parameter value, saving time.When
warm_startisTrue, the existing fitted model attributes is used to initialize the new model in a subsequent call tofit.n_components (
int, optional, default:None) – Number of components to keep.
See also
FastICAPerform Independent Component Analysis with a fast algorithm.
IRISIntegral inversion solver for spectroscopic data.
MCRALSPerform MCR-ALS of a dataset knowing the initial \(C\) or \(S^T\) matrix.
NMFNon-Negative Matrix Factorization.
PCAPerform Principal Components Analysis.
SIMPLISMASIMPLe to use Interactive Self-modeling Mixture Analysis.
SVDPerform a Singular Value Decomposition.
Examples
>>> # Init the model >>> model = scp.EFA() >>> # Read an experimental 2D spectra (N x M ) >>> X = scp.read("irdata/nh4y-activation.spg") >>> # Fit the model >>> _ = model.fit(X) >>> # Display components spectra (2 x M) >>> model.n_components = 2 >>> _ = model.components.plot(title="Component spectra") >>> # Get the abstract concentration profile based on the FIFO EFA analysis >>> c = model.transform() >>> # Plot the transposed concentration matrix (2 x N) >>> _ = c.T.plot(title="Concentration") >>> scp.show()
Initialize the BaseConfigurable class.
- Parameters:
log_level (int, optional) – The log level at startup. Default is logging.WARNING.
**kwargs (dict) – Additional keyword arguments for configuration.
Attributes Summary
Return the X input dataset (eventually modified by the model).
The
Yinput.Eigenvalues for the backward analysis (
NDDataset).NDDatasetwith components in feature space (n_components, n_features).traitlets.config.Configobject.Cut-off value.
Eigenvalues for the forward analysis (
NDDataset).Return
logoutput.Number of components to keep.
Object name
Methods Summary
fit(X)fit_transform(X, **kwargs)Fit the model with X and apply the dimensionality reduction on X.
get_components([n_components])Return the component's dataset: (selected n_components, n_features).
Not implemented.
parameters([replace, removed, default])Alias for
paramsmethod.params([default])Return current or default configuration values.
plotmerit([X, X_hat])Plot the input (
X), reconstructed (X_hat) and residuals.Not implemented.
reduce([X])Apply dimensionality reduction to
X.reset()Reset configuration parameters to their default values.
to_dict()Return config value in a dict form.
transform([X])Apply dimensionality reduction to
X.Attributes Documentation
- X
Return the X input dataset (eventually modified by the model).
- components
NDDatasetwith components in feature space (n_components, n_features).See also
get_componentsRetrieve only the specified number of components.
- config
traitlets.config.Configobject.
- cutoff
Cut-off value.
- log
Return
logoutput.
- n_components
Number of components to keep.
- name
Object name
Methods Documentation
- fit(X)[source][source]
Fit the
EFAmodel on aXdataset.- Parameters:
X (
NDDatasetor array-like of shape (n_observations, n_features)) – Training data.- Returns:
self – The fitted instance itself.
See also
fit_transformFit the model with an input dataset
Xand apply the dimensionality reduction onX.fit_reduceAlias of
fit_transform(Deprecated).
- fit_transform(X, **kwargs)[source][source]
Fit the model with X and apply the dimensionality reduction on X.
- Parameters:
X (
NDDatasetor array-like of shape (n_observations, n_features)) – Training data.**kwargs (keyword parameters, optional) – See Other Parameters.
- Returns:
NDDataset– Dataset with shape (n_observations, n_components).- Other Parameters:
n_components (
int, optional) – The number of components to use for the reduction. If not given the number of components is eventually the one specified or determined in thefitprocess.
- get_components(n_components=None)
Return the component’s dataset: (selected n_components, n_features).
- Parameters:
n_components (
int, optional, default:None) – The number of components to keep in the output dataset. IfNone, all calculated components are returned.- Returns:
NDDataset– Dataset with shape (n_components, n_features)
- parameters(replace="params", removed="0.7.1") def parameters(self, default=False)[source]
Alias for
paramsmethod.
- plotmerit(X=None, X_hat=None, **kwargs)[source]
Plot the input (
X), reconstructed (X_hat) and residuals.\(X\) and \(\hat{X}\) can be passed as arguments. If not, the
Xattribute is used for \(X`and :math:\)hat{X}`is computed by theinverse_transformmethod- Parameters:
X (
NDDataset, optional) – Original dataset. If is not provided (default), theXattribute is used and X_hat is computed usinginverse_transform.X_hat (
NDDataset, optional) – Inverse transformed dataset. ifXis provided,X_hatmust also be provided as compuyed externally.**kwargs (keyword parameters, optional) – See Other Parameters.
- Returns:
Axes– Matplotlib subplot axe.- Other Parameters:
colors (
tupleorndarrayof 3 colors, optional) – Colors forX,X_hatand residualsE. in the case of 2D, The default colormap is used forX. By default, the three colors areNBlue,NGreenandNRed(which are colorblind friendly).offset (
float, optional, default:None) – Specify the separation (in percent) between the \(X\) , \(X_hat\) and \(E\).nb_traces (
intor'all', optional) – Number of lines to display. Default is'all'.**others (Other keywords parameters) – Parameters passed to the internal
plotmethod of theXdataset.
- reduce(X=None, **kwargs)[source]
Apply dimensionality reduction to
X.- Parameters:
X (
NDDatasetor array-like of shape (n_observations, n_features), optional) – New data, where n_observations is the number of observations and n_features is the number of features. if not provided, the input dataset of thefitmethod will be used.**kwargs (keyword parameters, optional) – See Other Parameters.
- Returns:
NDDataset– Dataset with shape (n_observations, n_components).- Other Parameters:
n_components (
int, optional) – The number of components to use for the reduction. If not given the number of components is eventually the one specified or determined in thefitprocess.
Notes
Deprecated in version 0.6.
- transform(X=None, **kwargs)
Apply dimensionality reduction to
X.- Parameters:
X (
NDDatasetor array-like of shape (n_observations, n_features), optional) – New data, where n_observations is the number of observations and n_features is the number of features. if not provided, the input dataset of thefitmethod will be used.**kwargs (keyword parameters, optional) – See Other Parameters.
- Returns:
NDDataset– Dataset with shape (n_observations, n_components).- Other Parameters:
n_components (
int, optional) – The number of components to use for the reduction. If not given the number of components is eventually the one specified or determined in thefitprocess.
Examples using spectrochempy.EFA