Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
MCR-ALS with kinetic constraints¶
In this example, we perform the MCR ALS optimization of the UV-vis of spectra resulting
from a three-component reaction A -> B -> C which was investigated by UV–Vis
spectroscopy. Full details on the reaction and data acquisition conditions can be found
in Bijlsma et al. [2001] .
The data can be downloded from the author website Biosystems Data Analysis group
University of Amsterdam
(Copyright 2005 Biosystems Data Analysis Group ; Universiteit van Amsterdam )
import numpy as np
import spectrochempy as scp
Loading a NDDataset¶
DownLoad the data at
(Kinetic data set (UV-VIS) )
using the read function.
For sake of demonstration, we will focus on a single run.
For example, we extract only the data for the run #9 (dataset name: 'x9b' ).
Let’s search it. Data is a list of pairs of NDDataset, a pair of each run. The name we are looking for is the name of the second dataset in a apir.
now we have the required pair of dataset.
The first dataset incontains the time in seconds since the start of the reaction (t=0). The first column of the matrix contains the wavelength axis and the remaining columns are the measured UV-VIS spectra (wavelengths x timepoints)
print("\n NDDataset names: " + str([d.name for d in ds]))
NDDataset names: ['RelTime', 'x9b']
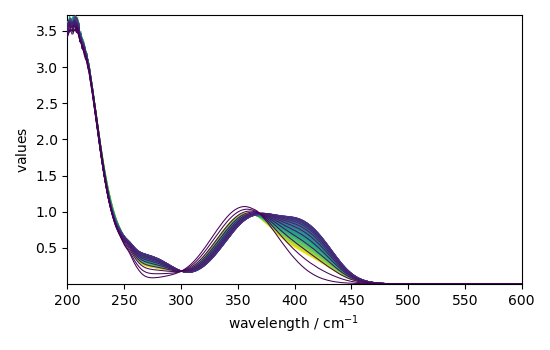
We load the experimental spectra (in ds[1]), add the y (time) and x
(wavelength) coordinates, and keep one spectrum of out 4:
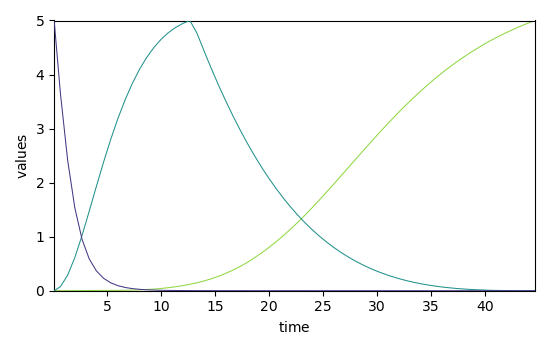
A first estimate of the concentrations can be obtained by EFA:
compute EFA...
We can get a better estimate of the concentration (C) and pure spectra profiles (St) by soft MCR-ALS:
mcr_1 = scp.MCRALS(log_level="INFO")
_ = mcr_1.fit(D, C0)
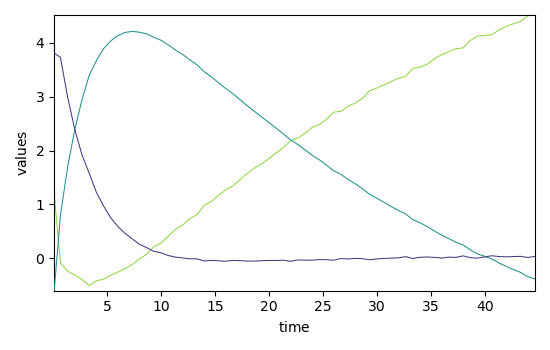
_ = mcr_1.C.T.plot()
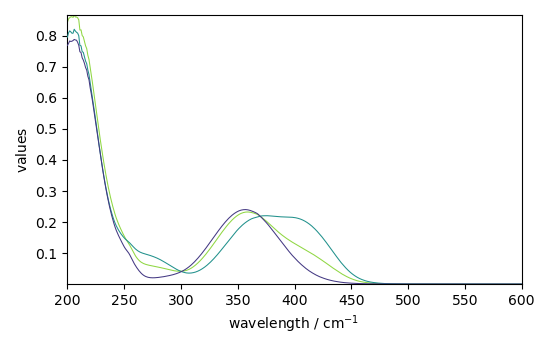
_ = mcr_1.St.plot()
Concentration profile initialized with 3 components
Initial spectra profile computed
*** ALS optimisation log ***
#iter RSE / PCA RSE / Exp %change
-------------------------------------------------
1 0.002813 0.005863 -99.286895
2 0.002810 0.005861 -0.020846
converged !
Kinetic constraints can be added, i.e., imposing that the concentration profiles obey a kinetic model. To do so we first define an ActionMAssKinetics object with roughly estimated rate constants:
reactions = ("A -> B", "B -> C")
species_concentrations = {"A": 5.0, "B": 0.0, "C": 0.0}
k0 = np.array((0.5, 0.05))
kin = scp.ActionMassKinetics(reactions, species_concentrations, k0)
The concentration profile obtained with this approximate model can be computed and compared with those of the soft MCR-ALS:
Ckin = kin.integrate(D.y.data)
_ = mcr_1.C.T.plot(linestyle="-", cmap=None)
_ = Ckin.T.plot(clear=False, cmap=None)
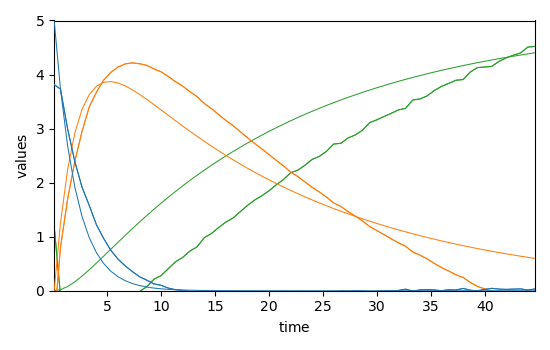
Even though very approximate, the same values can be used to run a hard-soft MCR-ALS:
X = D[:, 300.0:500.0]
param_to_optimize = {"k[0]": 0.5, "k[1]": 0.05}
mcr_2 = scp.MCRALS()
mcr_2.hardConc = [0, 1, 2]
mcr_2.getConc = kin.fit_to_concentrations
mcr_2.argsGetConc = ([0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2], param_to_optimize)
mcr_2.kwargsGetConc = {"ivp_solver_kwargs": {"return_NDDataset": False}}
mcr_2.fit(X, Ckin)
Optimization of the parameters.
Initial parameters: [ 0.5 0.05]
Initial function value: 6.457764
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 4.313287
Iterations: 28
Function evaluations: 54
Optimization time: 0:00:00.140123
Final parameters: [ 0.3975 0.05019]
Optimization of the parameters.
Initial parameters: [ 0.3975 0.05019]
Initial function value: 3.465589
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 2.678511
Iterations: 24
Function evaluations: 48
Optimization time: 0:00:00.118559
Final parameters: [ 0.3507 0.05016]
Optimization of the parameters.
Initial parameters: [ 0.3507 0.05016]
Initial function value: 2.257758
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 1.901765
Iterations: 23
Function evaluations: 46
Optimization time: 0:00:00.109222
Final parameters: [ 0.3244 0.05001]
Optimization of the parameters.
Initial parameters: [ 0.3244 0.05001]
Initial function value: 1.665581
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 1.482184
Iterations: 19
Function evaluations: 39
Optimization time: 0:00:00.090787
Final parameters: [ 0.3079 0.0498]
<spectrochempy.analysis.mcrals.MCRALS object at 0x7f15afba6580>
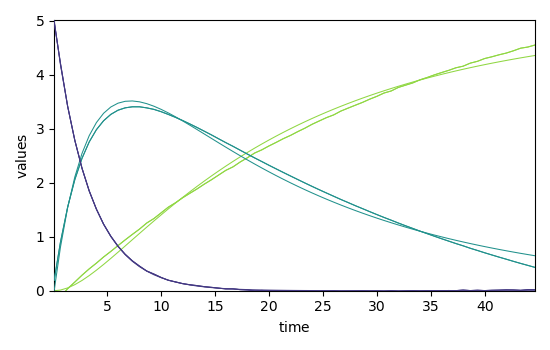
Now, let's compare the concentration profile of MCR-ALS
(C = X(C$_{kin}^+$ X)$^+$) with
that of the optimized kinetic model (C$_{kin}$ equiv$ C_constrained):
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 6
_ = mcr_2.C.T.plot()
_ = mcr_2.C_constrained.T.plot(clear=False)
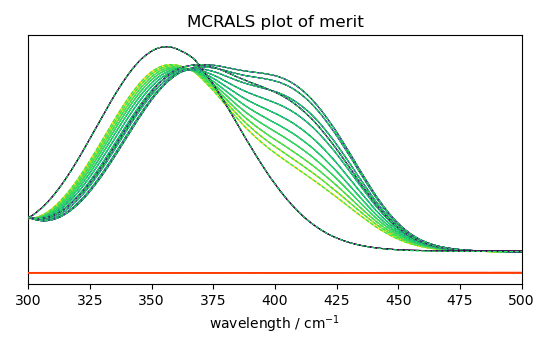
- Finally, let's plot some of the pure spectra profiles St, and the
reconstructed dataset (X_hat = C St) vs original dataset (X) and residuals.
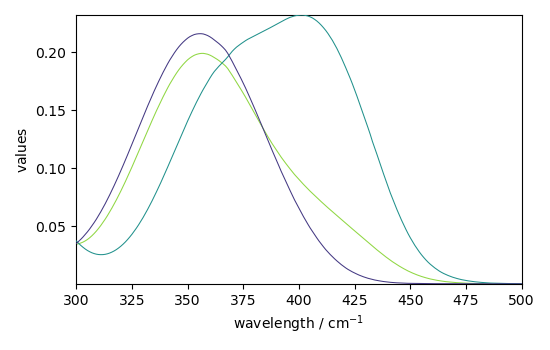
_ = mcr_2.St.plot()
_ = mcr_2.plotmerit(nb_traces=10)
This ends the example ! The following line can be uncommented if no plot shows when running the .py script
# scp.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 7.727 seconds)