Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Processing RAMAN spectra¶
Various examples of processing RAMAN spectra
Import API
import spectrochempy as scp
Importing a 1D spectra¶
Define the folder where are the spectra
datadir = scp.preferences.datadir
ramandir = datadir / "ramandata/labspec"
Read a single spectrum
A = scp.read_labspec("SMC1-Initial_RT.txt", directory=ramandir)
Plot the spectrum
_ = A.plot()
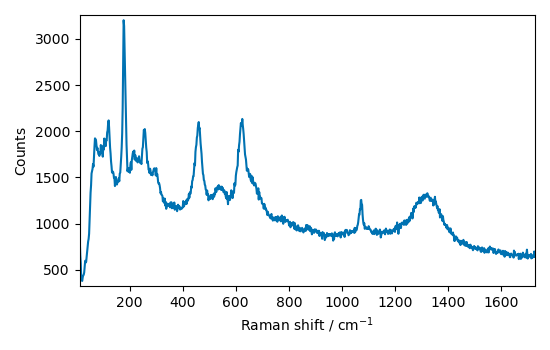
Crop the spectrum to a useful region
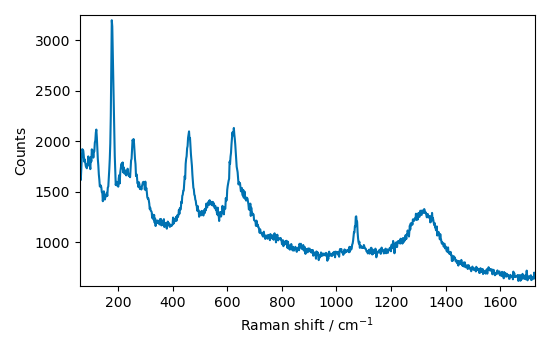
Baseline correction¶
Let’s try to remove the baseline using different methods
For this we use the Baseline processor
First, we define the baseline processor
blc = scp.Baseline(log_level="INFO")
Now we can try the various baseline methods.
Detrending¶
the detrend method is not strictly speaking a method to calculate a bottom line,
but it can be useful as a preprocessing to remove a trend.
Let’s define the model to be used for detrending
blc.model = "detrend"
Now we need to define the order of the detrending either as an integer giving the
degree of the polynomial trend or a string among { constant , linear ,
quadratic , cubic }
blc.order = "linear"
Now we can fit the model to the data
The baseline is now stored in the baseline attribute of the processor
Let’s plot the result of the correction
As we will use this type of plot several times, we define a function for it
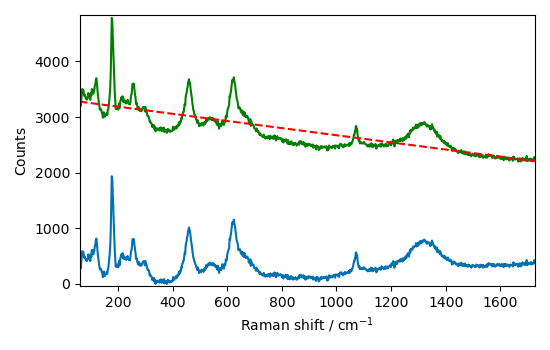
Let’s try with a polynomial detrend of order 2
blc.order = 2 # quadratic detrending
blc.fit(B)
corr = blc.transform()
baseline = blc.baseline
plot_result(B, corr, baseline)
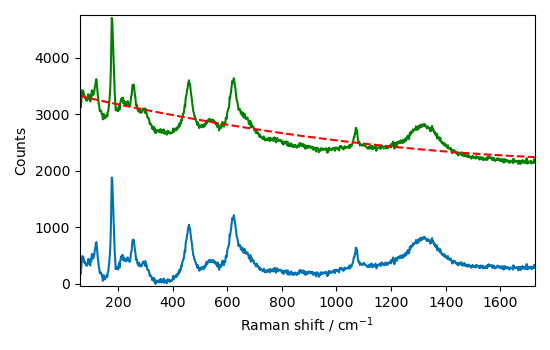
Ok this is a good start.
But we can do better with more specific baseline correction methods.
Let’s try the asymmetric least squares smoothing model ( asls ), on this detrended
spectrum:
Asymmetric Least Squares smoothing¶
blc.model = "asls"
We need to define the smoothness and asymmetry parameters. The smoothness parameter is a positive number that controls the smoothness of the baseline. The larger this number is, the smoother the resulting baseline. The asymmetry parameter controls the asymmetry for the AsLS resolution.
blc.lamb = 10**8 # smoothness
blc.asymmetry = 0.01
Now we can fit the model to the data
blc.fit(Bd)
corr = blc.transform()
baseline = blc.baseline
plot_result(Bd, corr, baseline)
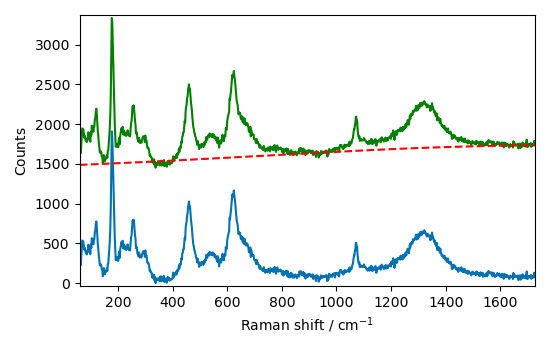
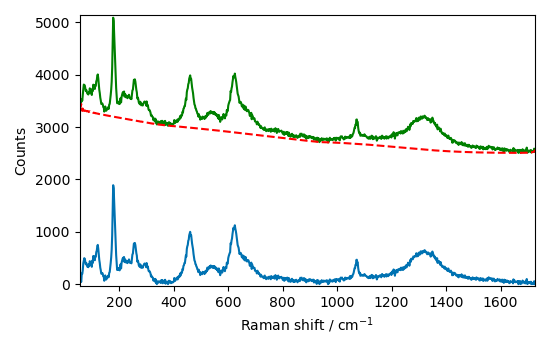
The correction appears to be good, but let’s see if we can do better by using the
snip method. This method requires to adjust the width of a window (usually set to
the FWHM of the characteristic peaks).
blc.model = "snip"
blc.snip_width = 55 # estimated FWHM of the peaks (expressed in point. TODO: alternatively use true coordinates)
Bs = A[55.0:]
blc.fit(Bs)
corr = blc.transform()
baseline = blc.baseline
plot_result(Bs, corr, baseline)
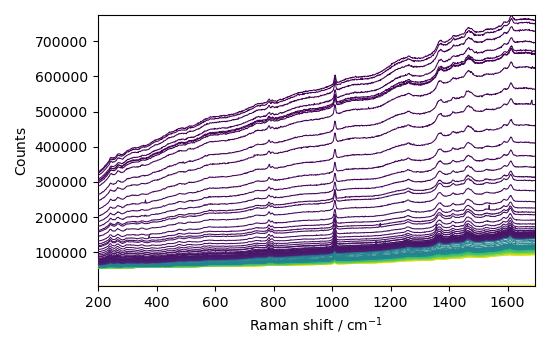
Baseline correction 2D spectra (series of spectra)¶
First, we read the series of spectra
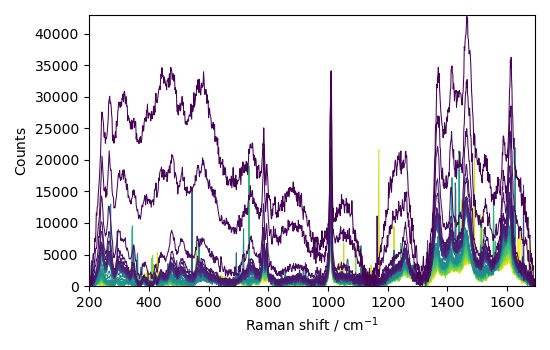
C = scp.read_labspec("Activation.txt", directory=ramandir)
# C = C[20:] # discard the first 20 spectra
_ = C.plot()
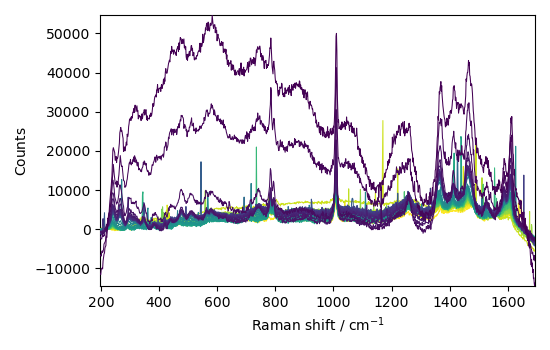
Now we apply the AsLS method on the series of spectra
We keep the same parameters as before and fit the new dataset The baseline is calculated for each spectrum of the series. So the process is very slow! For the demonstration we will the limit the series to 1 spectrum over 10.
blc.model = "asls"
blc.log_level = (
"WARNING" # supress output of asls (to long for the moment: TODO optimize this)
)
blc.fit(C[::10])
corr = blc.transform()
baseline = blc.baseline
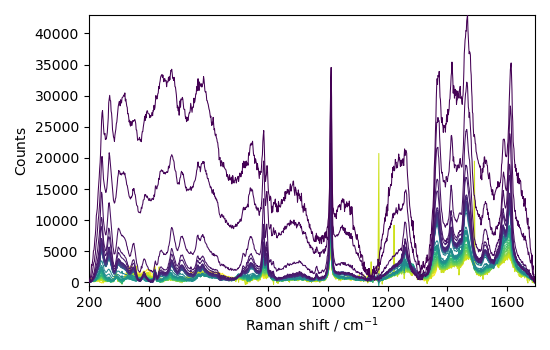
_ = corr.plot()
or the snip method (which is much faster)
blc.model = "snip"
blc.fit(C)
corr = blc.transform()
baseline = blc.baseline
_ = corr[::10].plot()
Denoising¶
This ends the example ! The following line can be removed or commented when the example is run as a notebook (*.ipynb).
# scp.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.883 seconds)