Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Removing cosmic ray spikes from a Raman spectrum
In this example, we use the despike method to remove the noise from a Raman
spectrum.
import spectrochempy as scp
Load the data
Keep only one spectrum in this series and select the useful region
Baseline correction the data using the fast ~spectrochempy.snip` algorithm
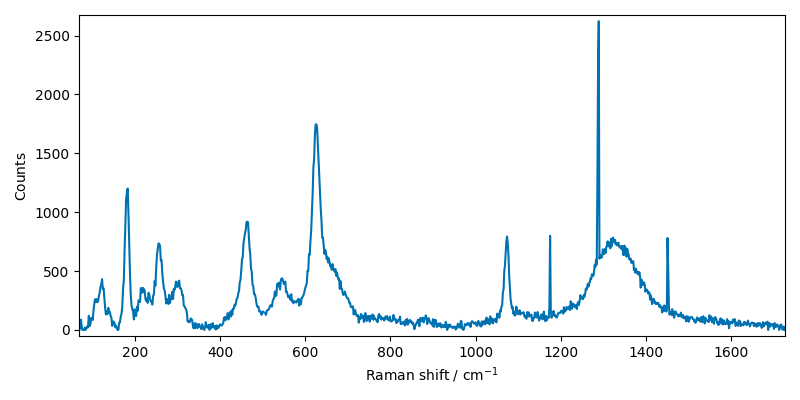
Plot the data
prefs = scp.preferences
prefs.figure.figsize = (8, 4)
X1.plot()
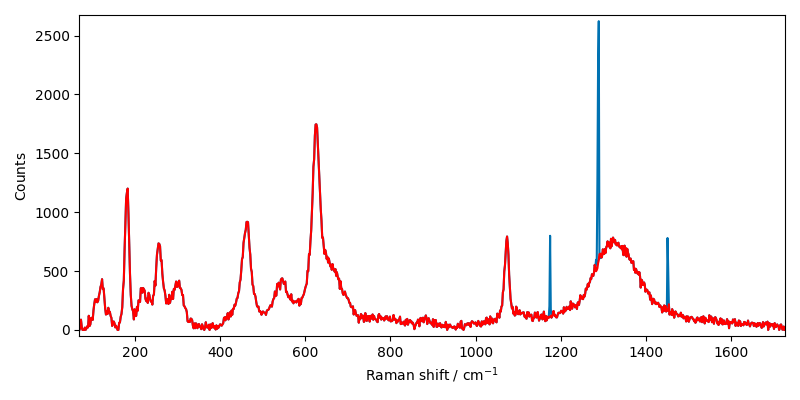
Now let’s use the despike method.
Only two parameters needs to be tuned: the size of the filter
(actually a Savitsky-Golay filter of order 2), and delta, the threshold for the
detection of spikes (outliers).
A spike is detected if its value is greater than delta times the standard deviation
of the difference between the original and the smoothed data.
X2 = scp.despike(X1, size=11, delta=5)
X1.plot()
X2.plot(clear=False, ls="-", c="r")
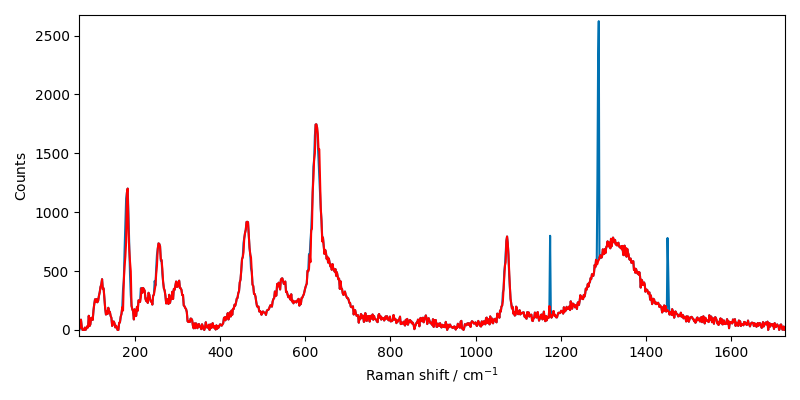
Another method, ‘whitaker’, is also available (see the documentation for details): %%
X3 = scp.despike(X1, size=11, delta=5, method="whitaker")
X1.plot()
X3.plot(clear=False, ls="-", c="r")
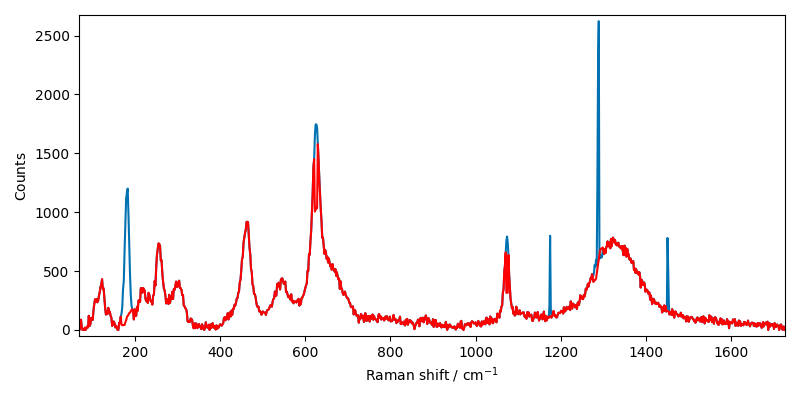
Getting the desired results require the tuning of size and delta parameters. And sometimes may need to repeat the procedure on a previously filtered spectra.
For example, if size or delta are badly chosen, valid peaks could be removed. So careful inspection of the results is crucial.
X4 = scp.despike(X1, size=21, delta=2)
X1.plot()
X4.plot(clear=False, ls="-", c="r")
This ends the example ! The following line can be uncommented if no plot shows when running the .py script with python
# scp.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.610 seconds)